Chapter 5: Synchronization
Race Conditions and Locks #
If two independent threads need to modify and read the same values, there could be multiple outputs depending on the order that the threads run in. How do we resolve this?
Synchronization deals with coordination among threads and their shared data
Mutual Exclusion: Only one thread does something at one time (excludes the other threads)
- Subtype of synchronization
Critical Section: code that only one thread can execute at once (consequence of mutual exclusion)
High Level Concurrency API #
Locks #
Lock: An object that only one thread can hold at a time (provides mutual exclusion)
lockacquire()orpthread_mutex_lockwaits until lock is free, then marks as busylockrelease()orpthread_mutex_unlockfrees a lock (calling thread no longer holds the lock)
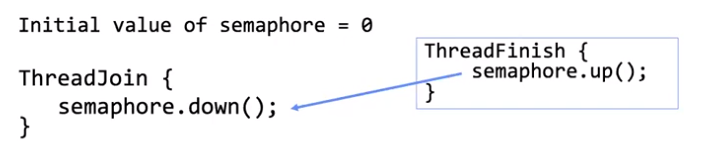
Semaphores #
A general type of lock that holds a non-negative integer.
P()ordown(): waits for semaphore to be positive, then decrements by 1V()orup(): increments semaphore by 1
Can be used for mutual exclusion by setting it down, running critical section, then setting it up.

Semaphores can also be used for signaling other threads: