Collections
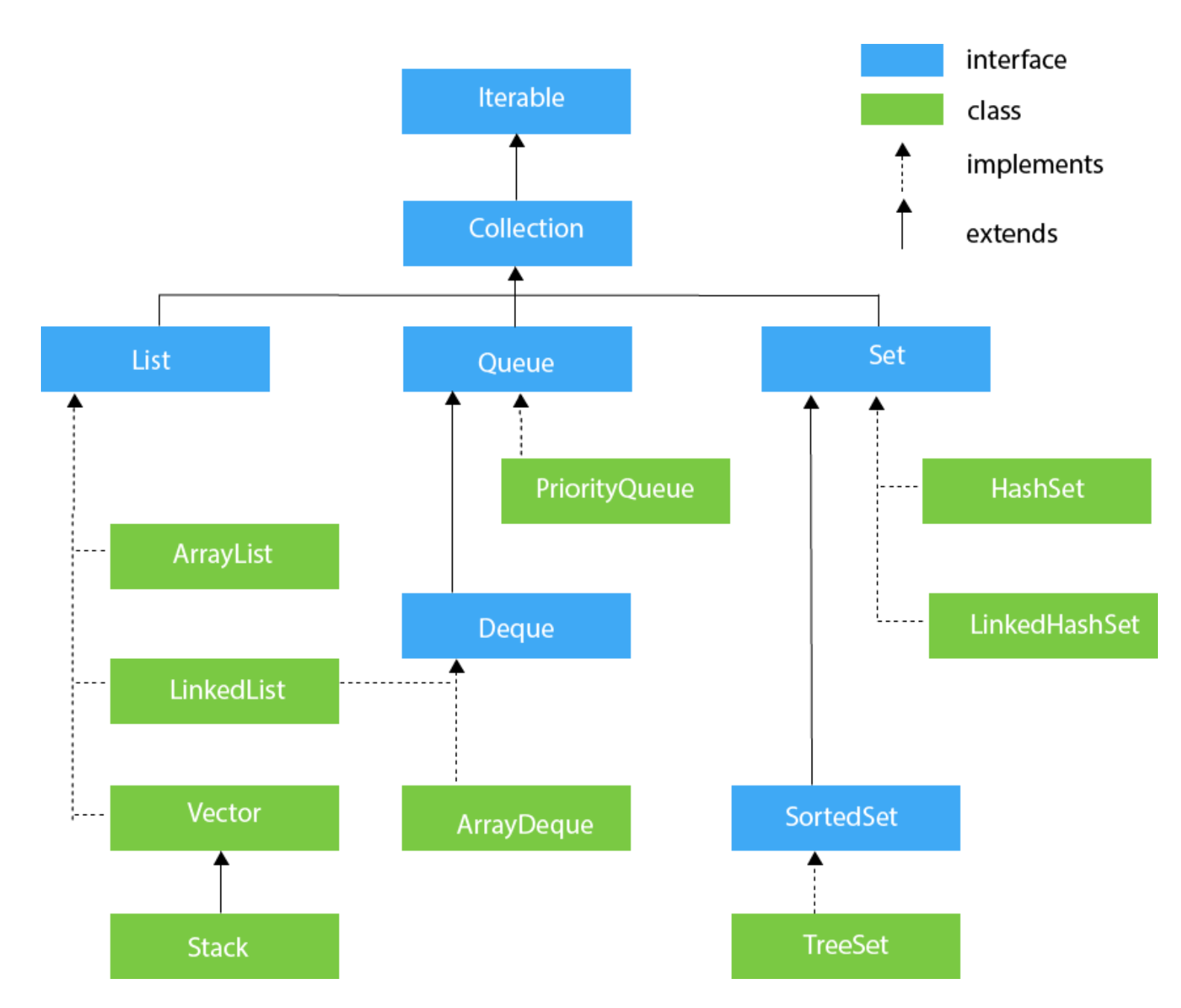
Collection is a Java interface for common abstract data types that store multiple items in them.
Sub-Interfaces #
- Lists are indexed sequences with duplication. The two most common types are
ArrayListsand Linked Lists
Content Note > This page assumes prior knowledge of Python lists from CS61A or equivalent. Arrays are a very popular data structure...
.Content Note > This page assumes prior knowledge of linked lists from CS61A or equivalent. I'll assume you have already worked...
- Setsare non-indexed sequences with no duplication. (That is, every value in a set is unique.)
Warning > This page is incomplete. help make it better! Basics A Set stores a collection of values with no duplicates. Sets have...
- Maps are key-value pairs. See
Hashing and Hash Tablesfor a description on one common map implementation, the HashMap. All keys in a map must be unique, but values can be duplicated.
Hashing and Hash Tables
Data Indexed Sets: Introduction So far, we've explored a whole bunch of ways we can store items, but they aren't really...
- Stacks and Queuesare two ordered collections that have two core behaviors:
Stacks and queues are two very common data structures used for a variety of applications from CPU processes to finding...
- push(T x): puts x on the top.
- pop(): Removes the first item. (See the stacks and queues page for more information.)
Common Functions #
- Membership tests
contains()andcontainsAll()that can determine whether or not an element is in the collection. size()to get the number of items in the collection.isEmpty()returns true if there is nothing in the collection.iterator()returns an Iterator object to go through all the values in the collection.toArray()converts the collection to a standard Java array.- Optional functions that aren’t implemented in the interface:
add, addAll, clear, remove, removeAll, retainAll (intersection)- Throws
UnsupportedOperationExceptionif not implemented.
- Throws