CS 186: Databases
Welcome to my CS186 Guide! #
This is a non-comprehensive guide to databases written with an intention to supplement learning and reviewing of Berkeley’s CS186 material. Main topics include:
- SQL syntax
SQL Basics
Relevant Materials Note 1 Note 2 Discussion 1 What is SQL? Structured Query Language (/ˈsiːkwəl/) is a highly standardized syntax for performing...
- How to improve popular sorting and hashing algorithms to work well with limited memory
Sorting and Hashing
Introduction When dealing with disk operations, traditional sorting algorithms tend to create lots of random accesses and can be quite slow....
- B+ treesand other advanced indexing structures
B+ Trees
Relevant Materials Note 4 Discussion 3: view this for B+ tree algorithm walkthroughs! Introduction B+ Trees are one type of index: a...
- Join algorithms
Iterators and Joins
Introduction As you may have seen already, some SQL queries involve joining lots of tables together to get the data we...
- Query optimization
Query Optimization
Introduction Query optimization is the bridge between a declarative language (like SQL, where you describe “what” you want) and an imperative...
- Parallel query processing
Parallel Query Processing
Relevant Materials Note 15 Discussion 11 Parallelism Parallelism helps us break down a big problem into small, independent chunks. The idea is...
- Crash Recovery (AERIES)
Recovery
Introduction Recovery is the process of making databases resilient to failure. Specifically, recovery enforces durability (a committed transaction remains persistent) and...
- Database transactions and Concurrency
Transactions and ACID
What is a transaction? Transactions are collections of operations that can be treated like a single unit. The primary reason why...
- Entity-Relationship Diagrams
E-R Diagrams
Introduction Production databases have a lot of tables with complicated relationships. Entity Relationship (ER) Diagrams help us organize databases in a...
I recognize that the course notes for 186 can be very dense sometimes, and don’t cover 100% of the information you need to do well on projects and exams. While this also doesn’t covery everything, I try to focus on content that the notes don’t.
This isn’t a replacement for lectures and other course content. You probably need to look at those first, and come here if something isn’t sticking!
Please read this first!
Disclaimer #
Although I am a 186 TA, these notes are not official course content. They have not been reviewed or approved by an instructor, and there may be inaccurate or missing information. Please don’t bother the other course staff with questions about the content here- contact me instead (email or office hours).
Concept Maps #
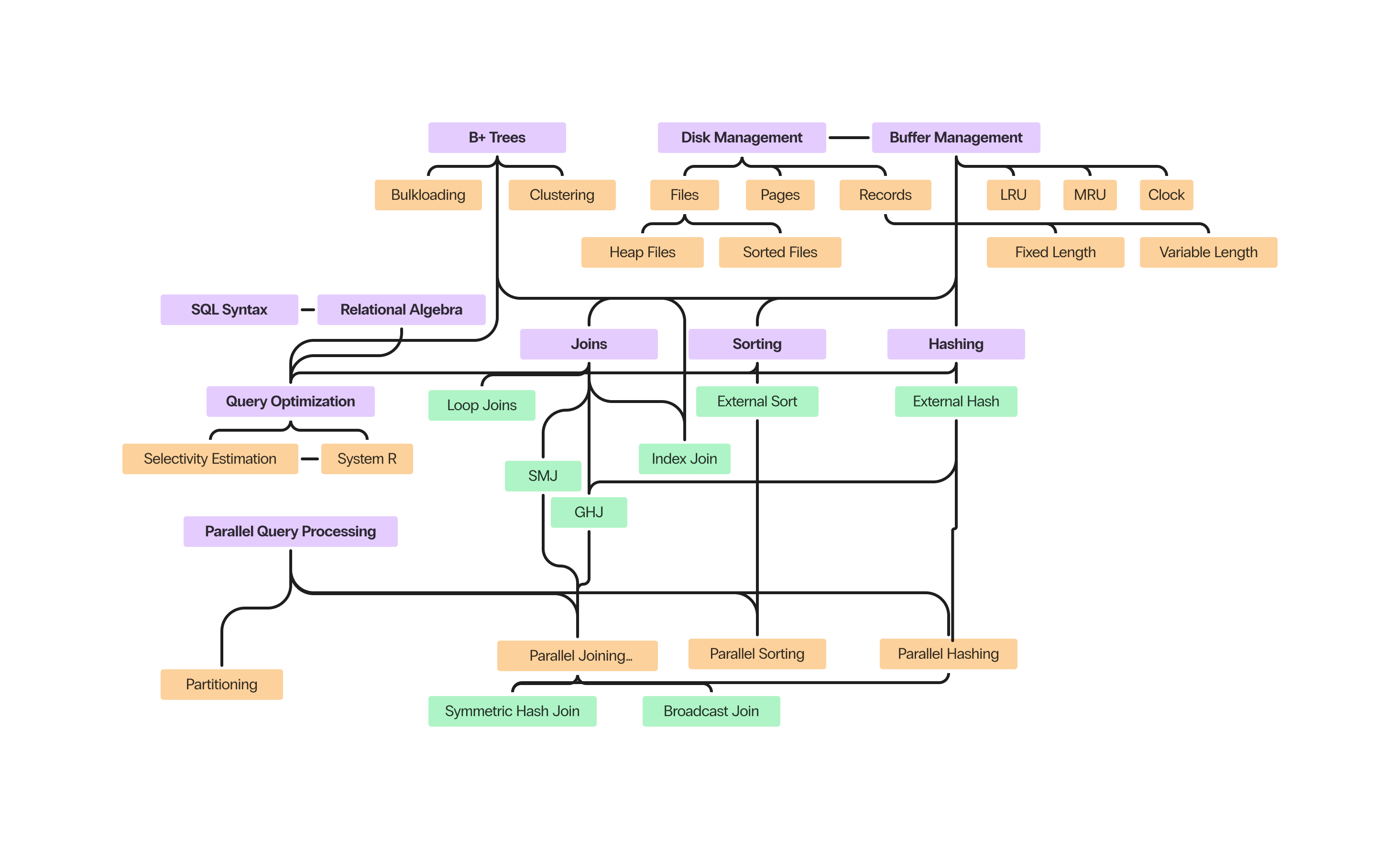
Database Implementation #
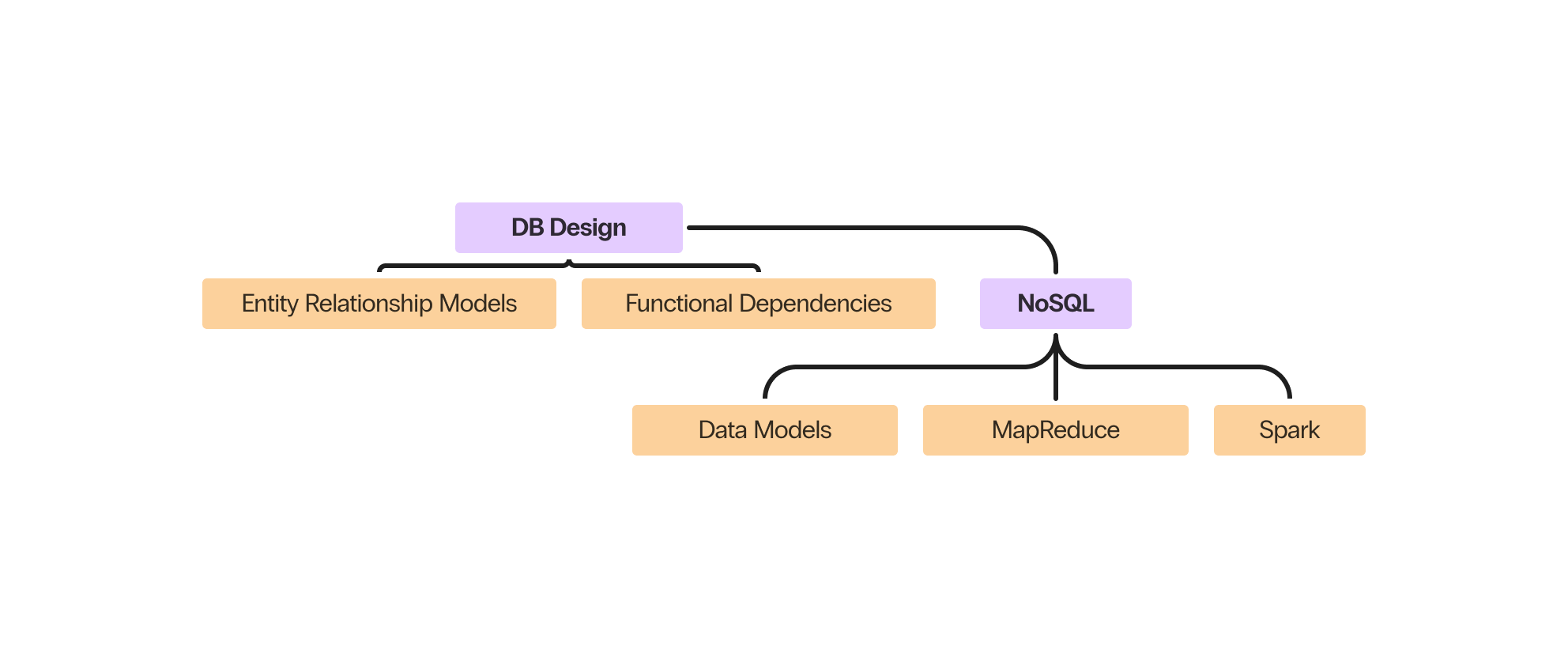
Database Design #
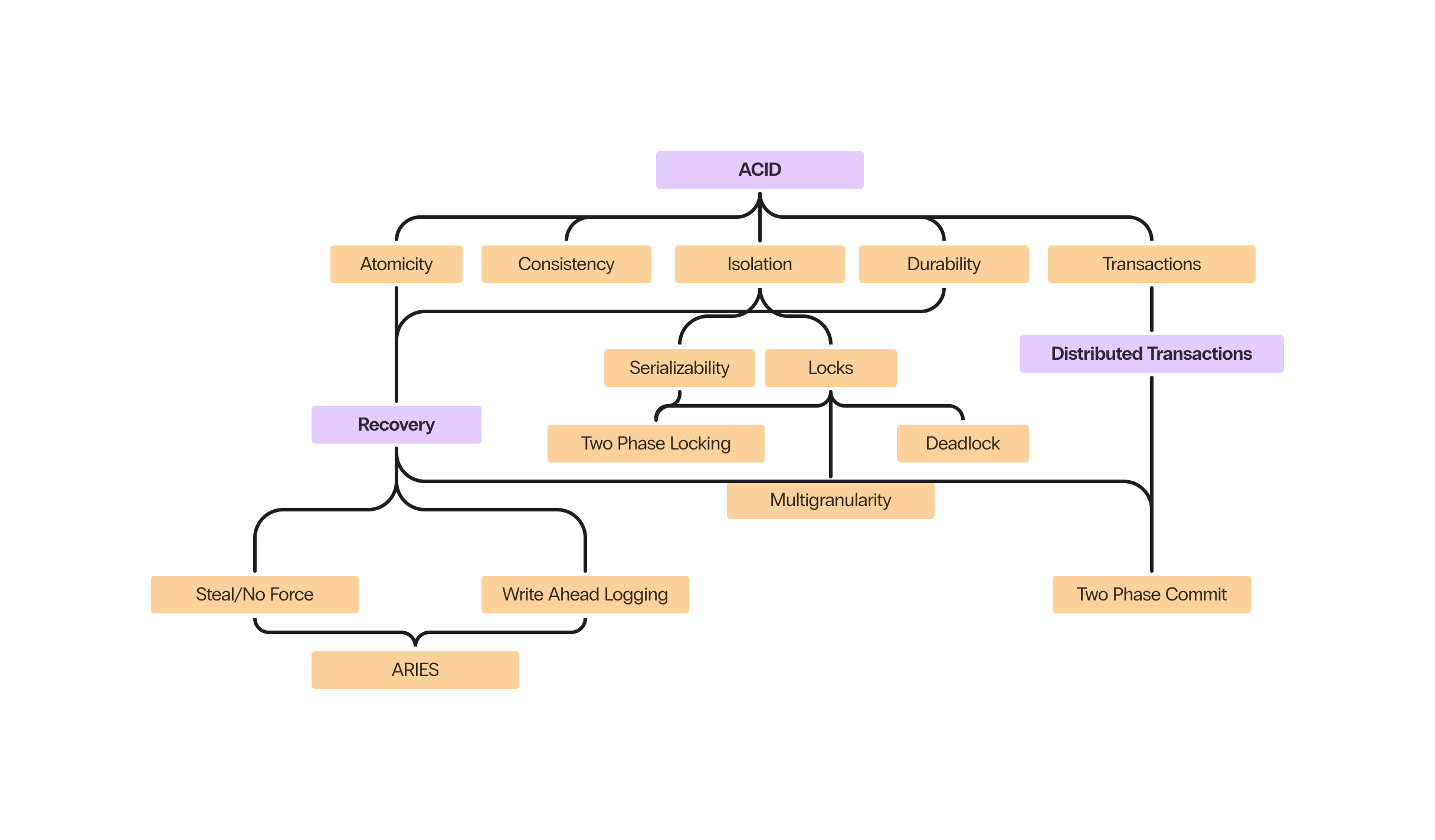
ACID #
Prerequisites #
CS 186 projects are done in Java. Knowledge of CS61B concepts are assumed. Specifically, you should understand:
- OOP fundamentals such as classes, inheritance, and objects and implement them in Java
- Binary trees, their runtime proprties, and implementation of efficient search and insert algorithms
- Basic hashing and sorting algorithms
- Use an IDE (preferably IntelliJ or VSCode) and its debugger to step through code and create breakpoints
In addition, knowledge from the last part of CS61C is assumed and will be very useful for the first part of 186. This includes:
- Knowing how computers store memory, the different types of memory (disk, RAM, cache), and why we have them
- How data is stored on disk (files, pages, records)
Unsure about prerequisite content? You can review my
CS61B notes if needed. I’ll cover the main points from 61C at the start of
Disks, Buffers, Files
Relevant Materials
Note 3
Discussion 2
Introduction
Now that we've taken a look at how humans can interface with databases using SQL,...Disks, Buffers, and Files
How to contribute #
See the
contributing guide
Thanks for your interest in contributing to my notes! There's a lot of room for improvement, and I don't have...Contributing
Two particular additions that need to be made are entries for Functional Dependencies and NoSQL. I don’t have notes written for this since these topics were not covered when I took the course.